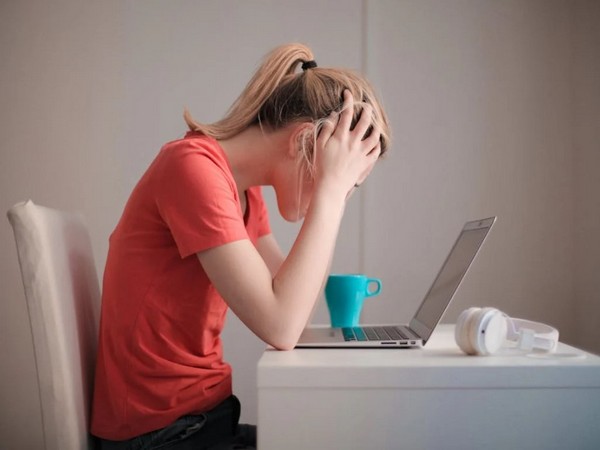
Toronto [Canada], November 15 (ANI): Researchers at The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) revealed that stress alters how our brain encodes and retrieves aversive memories, and they developed a potential new method for restoring adequate memory specificity in persons suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
If you stumble during a presentation, you might feel stressed the next time you have to present because your brain associates your next presentation with that one poor and aversive experience. This type of stress is tied to one memory. But stress from traumatic events like violence or generalized anxiety disorder can spread far beyond the original event, known as stress-induced aversive memory generalization, where fireworks or car backfires can trigger seemingly unrelated fearful memories and derail your entire day. In the case of PTSD, it can cause much greater negative consequences.
In a study published in Cell, Drs. Sheena Josselyn and Paul Frankland, Senior Scientists in the Neurosciences & Mental Health program, identify the biological processes behind stress-induced aversive memory generalization and highlight an intervention which could help restore appropriate memory specificity for people with PTSD.
“A little bit of stress is good, it’s what gets you up in the morning when your alarm goes off, but too much stress can be debilitating,” says Josselyn, who holds a Canada Research Chair in Circuit Basis of Memory. “We know that people with PTSD show fearful responses to safe situations or environments, and have found a way to limit this fearful response to specific situations and potentially reduce the harmful effects of PTSD.”
Together with their colleague Dr. Matthew Hill at the University of Calgary Hotchkiss Brain Institute, the research team was able to block endocannabinoid receptors on interneurons, and limit stress-induced aversive memory generalization to the specific, appropriate memory.
In a preclinical model, the research team exposed subjects to an acute, but safe, stress before an aversive event to create a non-specific fearful memory that could be triggered by unrelated safe situations, similar to how PTSD presents in humans.
The team then examined the subject’s memory engrams, which are physical representations of a memory in the brain pioneered by the Josselyn and Frankland labs at SickKids. Usually, engrams are made up of a sparse number of neurons, but the stress-induced memory engrams involved significantly more neurons. These larger engrams produced generalized fearful memories that were retrieved even in safe situations.
When they looked closer at these large engrams, the study found that stress caused an increase in the release of endocannabinoids (endogenous cannabinoids) which disrupted the function of interneurons, whose role is it to constrain the size of the engram.
The endocannabinoid system enhances memory formation and helps link lived experiences with specific behavioural outcomes. In the amygdala, the emotional processing centre of the brain, certain ‘gate keeper’ interneurons have special receptors for endocannabinoids, and help constrain the size of the engram and the specificity of the memory. But, when too many endocannabinoids are released, the function of the gatekeeping interneurons is disrupted, causing an increase in the size of the engram.
“Endocannabinoid receptors function like a velvet rope at an exclusive club. When stress induces the release of too many endocannabinoids, the velvet rope falls, causing more generalized aversive fearful memories to form,” explains Josselyn. “By blocking these endocannabinoid receptors just on these specific interneurons, we could essentially prevent one of the most debilitating symptoms of PTSD.”
In 2023, previous research in Science identified larger, more generalized memory engrams in the developing brain than in the adult brain, just like stress-induced memory engrams. As they continue to explore this unexpected link between engram size, stress and age, the teams are also delving into how daily stressors may impact happy memories.
“The many biological functions and processes that make up the complexity of human memory are still being uncovered,” says Frankland, who holds a Canada Research Chair in Cognitive Neurobiology. “We hope that as we better understand human memory, we can inform real-world therapies for those with various psychiatric and other brain disorders throughout their lifespan.” (ANI)
Disclaimer: This story is auto-generated from a syndicated feed of ANI; only the image & headline may have been reworked by News Services Division of World News Network Inc Ltd and Palghar News and Pune News and World News
HINDI, MARATHI, GUJARATI, TAMIL, TELUGU, BENGALI, KANNADA, ORIYA, PUNJABI, URDU, MALAYALAM
For more details and packages